~6.5까지의 강의. 끝 !
이제 코드를 정리해보자.
먼저. Home에 있는 form을 NweetFactory를 만들어 정리한다.
Home.js
import React,{useState, useEffect } from "react";
import { dbService, storageService } from "fbase";
import Nweet from "components/Nweet";
import NweetFactory from "components/NweetFactory";
const Home = ({ userObj }) => {
const [nweets, setNweets] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => { dbService.collection("nweets").onSnapshot((snapshot) => {
const nweetArray = snapshot.docs.map((doc) => ({
id: doc.id,
...doc.data(),
}));
setNweets(nweetArray);
});
}, []);
return (
<div>
<NweetFactory userObj={userObj} />
<div>
{nweets.map((nweet) => (
<Nweet
key={nweet.id}
nweetObj={nweet}
isOwner={nweet.creatorId === userObj.uid}
/>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;
NweetFactory.js
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid";
import { storageService, dbService } from "fbase";
const NweetFactory = ({ userObj }) => {
const [nweet, setNweet] = useState("");
const [attachment, setAttachment] = useState("");
const onSubmit = async (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
let attachmentUrl = "";
if (attachment !== "") {
const attachmentRef = storageService
.ref()
.child(`${userObj.uid}/${uuidv4()}`);
const response = await attachmentRef.putString(attachment, "data_url");
attachmentUrl = await response.ref.getDownloadURL();
}
const nweetObj = {
text: nweet,
createdAt: Date.now(),
creatorId: userObj.uid,
attachmentUrl,
};
await dbService.collection("nweets").add(nweetObj);
setNweet("");
setAttachment("");
};
const onChange = (event) => {
const {
target: { value },
} = event;
setNweet(value);
};
const onFileChange = (event) => {
const {
target: { files },
} = event;
const theFile = files[0];
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onloadend = (finishedEvent) => {
const {
currentTarget: { result },
} = finishedEvent;
setAttachment(result);
};
reader.readAsDataURL(theFile);
};
const onClearAttachment = () => setAttachment(null);
return (
<form onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<input
value={nweet}
onChange={onChange}
type="text"
placeholder="What's on your mind?"
maxLength={120}
/>
<input type="file" accept="image/*" onChange={onFileChange} />
<input type="submit" value="Nweet" />
{attachment && (
<div>
<img src={attachment} width="50px" height="50px" />
<button onClick={onClearAttachment}>Clear</button>
</div>
)}
</form>
);
};
export default NweetFactory;
그리고, Auth로 간다.
form을 담을 별개의 파일을 담을 AuthForm을 만든다.
Auth.js
import { authService, firebaseInstance } from 'fbase';
import React,{useState} from 'react';
import AuthForm from "components/AuthForm";
const Auth = () => {
const onSocialClick = async (event) => {
const {
target: { name },
} = event;
let provider;
if (name === "google") {
provider = new firebaseInstance.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
} else if (name === "github") {
provider = new firebaseInstance.auth.GithubAuthProvider();
}
await authService.signInWithPopup(provider);
};
return (
<div>
<AuthForm />
<div>
<button onClick={onSocialClick} name="google">
Continue with Google
</button>
<button onClick={onSocialClick} name="github">
Continue with Github
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Auth;
AuthForm.js
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { authService } from "fbase";
const AuthForm = () => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
const [newAccount, setNewAccount] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState("");
const onChange = (event) => {
const {
target: { name, value },
} = event;
if (name === "email") {
setEmail(value);
} else if (name === "password") {
setPassword(value);
}
};
const onSubmit = async (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
try {
let data;
if (newAccount) {
data = await authService.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(
email,
password
);
} else {
data = await authService.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email, password);
}
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
setError(error.message);
}
};
const toggleAccount = () => setNewAccount((prev) => !prev);
return (
<>
<form onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<input
name="email"
type="email"
placeholder="Email"
required
value={email}
onChange={onChange}
/>
<input
name="password"
type="password"
placeholder="Password"
required
value={password}
onChange={onChange}
/>
<input
type="submit"
value={newAccount ? "Create Account" : "Sign In"}
/>
{error}
</form>
<span onClick={toggleAccount}>
{newAccount ? "Sign In" : "Create Account"}
</span>
</>
);
};
export default AuthForm;
그리고 로그아웃을 위해 App에 null을 추가한다.
App.js
useEffect(() => {
authService.onAuthStateChanged((user) => {
if (user) {
setUserObj({
displayName: user.displayName,
uid: user.uid,
updateProfile: (args) => user.updateProfile(args),
});
} else {
setUserObj(null);
}
setInit(true);
});
}, []);
이제 배포를 해보자!
github page로 배포해보자.(사실 전에 했었음)
package.json으로 간다.
1. git remote-v를 입력해서 저장소가 어디인지 확인해본다.(나는 organization에 있어서 앞에 Co-buying이 붙음)

2. 나온 주소를 package.json의 맨 밑에 입력한다.

3. npm i gh-pages
4. scripts로 가서 deploy와 predeploy를 추가한다.
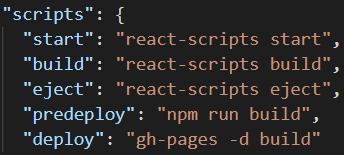
deploy시 npm run build라고 하면 build가 만들어진다.
그 후에 gh-pages.
5. npm run deploy
빌드후에 우리의 홈페이지로 업로드 해준다.
보안 규칙을 적용해보자.
보안규칙 하나는 특정 도메인에서만 로그인이 가능하다는 것이다.
다음으로는, Security Rules이다.
1.
Firebase console -> Authentication -> Sing-in method
승인된 도메인에 우리가 배포한 깃허브 사이트가 들어가있지 않다.
배포한 도메인을 '승인된 도메인'에 추가한다.
이렇게 하면 , 다른 웹 사이트에서도 로그인이 가능해진다.
2.
FireStore에 들어가보면, 규칙들을 확인할 수 있다.
근데 우리는 처음에 test용으로 해서, test용 규칙을 확인할 수 있다.
다양한 건 문서에서 확인할 수 있다.

즉 로그인이 되어있으면 글을 쓸 수 있게 한다는 의미이다.
같은 것을 Storage에도 적용할 수 있다.
근데 이미 전에 바꿔놓았음.
그 다음에는 https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials로 들어간다.
그리고, 프로젝트를 선택한다.
여기서 API keys를 좀 더 보안이 되도록 해보자.
1. Browser key를 선택한다.
2. HTTP를 선택하고, 사이트 주소를 추가한다.
3. localhost도 추가한다.
4. Firebase의 도메인도 추가한다.(Authentication -> Sign-in method 에 있음)
4번이 로그인 과정을 다루어 준다.
이것을 통해서 오로지 우리가 추가한 곳에서만 요청을 받을 수 있다.
그리고 Web client key가 있는데, 이것도 같은식으로 할 수 있다.
'Web Service > React' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Realtime Database] Setting (0) | 2023.05.17 |
|---|---|
| [실전형 리액트 Hooks] #1. INTRODUCTION (0) | 2023.01.11 |
| [트위터 클론 코딩] #8. Edit (0) | 2022.05.06 |
| [트위터 클론 코딩] #7. File Upload (0) | 2022.04.10 |
| [트위터 클론 코딩] #6. Preview Images (0) | 2022.04.03 |




댓글